- Markets
- Products
- Services and Solutions
- About Nexans
- People and Carreer
- News
- Certificates and Documents
- Nexans Insights
- Search
- Contact us
- Compare
- Sign in
Segurança e Conformidade - Folha informativa

Megatrend in Sustainable Electrification
It’s an exciting time to work with energy: The future is electric! The world will be electrified and carbon neutral by 2050. Electrification of the world is key to sustainable, balanced, and equitable growth that benefits all humanity. This transition means that global energy demand is set to increase by around 40% by 2030.
But what does Sustainable Electrification mean?
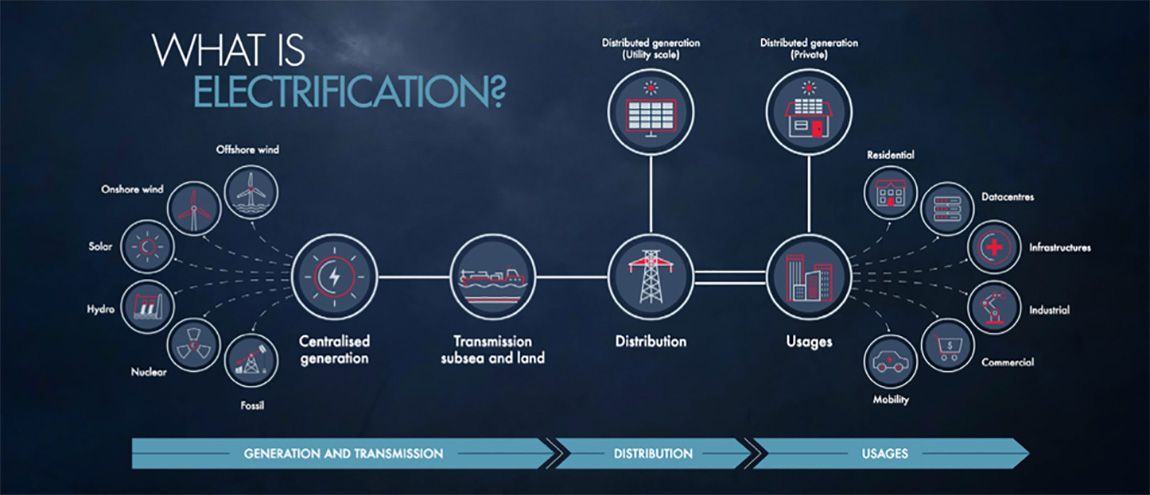
The idea of global electrification involves the creation of an energy value chain covering generation, transmission, distribution, and usage:
-
Generation: is the initial phase where the world’s energy is produced. This can involve many different technologies, such as offshore and onshore wind farms, solar farms, hydropower schemes, and nuclear power plants.
-
Transmission: is the second stage in which energy is transmitted from where it is generated to large consumption centers. It can take place over long distances, between countries and regions over land or under the sea.
-
Distribution: is the stage where the energy generated is received and distributed to the end-users. This area currently requires significant modernization of existing infrastructure to handle more complex power flows to ensure security of supply.
-
Usage: is the last stage, concentrated in the end-user consumption and driving the demand for electricity wherever there is human activity: construction, data centers, infrastructure, industrial activities, commercial businesses, etc.
The potential for the electrification sector is huge (> 150 billion Euros), and countries around the world are setting out on projects of unprecedented scale and capacity.
Let’s focus on Usage…
Usage of electricity is everywhere around us: wherever there is human activity – in all buildings (residential, commercial, industrial); public buildings such as schools and hospitals; in all means of transportation such as railway stations, airport terminals, marine ports, even e-mobility; and datacenters for which electricity supply is as critical as data connectivity.
Nexans has always been part of the history of electricity, playing a crucial role in the electrification of the world, which gives it its purpose: Electrify the future. This is why Nexans is committed to becoming a pure electrification player in this ecosystem. In the Usage framework, it means that Nexans provides end-to-end supply chain services and product innovation to ease installation. It also enhances safety and installer productivity supported by smart cables and accessories.
The Usage market is dynamic, with significant growth in cable demand of 50% over the next 10 years, representing an increase of around €26 billion (from €55 billion to €81 billion). This significant growth is driven by megatrends worldwide: a growing population (+1.8 billion people to have access to energy by 2030) and urbanization. We will have > 40 megacities around the world by 2030, increasing access to electrification in rural areas.
There are some key market challenges in the Usage market, such as safety (from products to installation), environment (from renewable energy to scarcity of resources), and end-to-end supply chain. This brings us to the next question on...
The market challenges in safety
As a consequence of the increased demand for electricity, installations are mostly undersized, increasing the risks for electrical fires. Older buildings across the world are particularly vulnerable since they have been sized for much lower electricity absorption.
While installations had been well dimensioned during 60s and 70s, nobody ever envisaged that power demand would soar to record highs in just 50 years. Today most of these buildings require major renovation investment. This is one reason why safe electrical power usage is and will be at the heart of our philosophy.
80% of building fires in emerging countries are due to non-compliant cables.
273,000 In Europe, a fire happens every 6 minutes due to electrical failures, representing 273,000 fires per year.
25-30% of domestic fires in the EU are caused by an electrical origin. These risks are usually related to electrical appliances as well as to deteriorated connections with switches and other terminals.
In the European Economic Area, there is, since 2017, a common technical language that intends to ensure alignment among all products that circulate in the zone. This is called the “Construction Products Regulation” or CPR and is based on the main classification criteria regarding the product’s fire reaction, such as heat release and flame spread or propagation. There are also additional criteria for smoke density, flaming droplets, and smoke acidity. The regulation is intended to help compare different products so that the most suitable product gets selected for specific installations.
On the other hand, for countries outside Europe, our products also meet with other international standards, such as the IEC for example, that is essential for quality and risk management; following this set of norms allow the manufacturers to produce products of consistent quality and performance. In general, at this point, we can say that we meet with the most rigorous and highest local and international standards.
Common building cables often use materials that emit heavy smoke and hazardous fumes when burning, making evacuation difficult. So, then, the choice of appropriate cables becomes critical for people’s safety.
Nexans’ offer and expertise
We believe that safety starts with cables. They can ensure the supply of power and the continuity of data transmission. They can also contribute to increasing the time available for people to escape a fire.
Based on the behavior of our fire safety cables during a fire, they can be classified into two categories:
-
Fire-resistant cables that can withstand high temperatures and extend the operating time while still transmitting the electric power and communication signals.
-
Low Fire-Hazard cables that ensure minimal smoke production and acidity of emissions, prevent flames from spreading, and reduce heat release.
Common building cables often use materials that emit heavy smoke and hazardous fumes when burning, making evacuation difficult. That’s why it’s also the cause of the majority of deaths in a fire. Therefore, it is vital to reduce the exposure time to these emissions by facilitating safe evacuation with the best possible visibility.
A low level of opacity of smoke produced and acidity of the emissions are basic criteria in selecting materials that, in the event of a fire, make it possible to reduce the presence of dangerous gases and to facilitate escape.
On the other hand, fire-resistant cables are an essential component of any alarm circuit. During fires, buildings should remain functional to help in the evacuation process. The safety of people is the priority: fire safety equipment like warning systems, smoke detectors, smoke extractors, emergency exits, and fire fighting equipment are crucial and must remain functional. Fire resistant cables are the backbone of all this equipment.
Nexans owns +150 fire safety-related patents and has a complete portfolio of products compliant with international regulation on fire safety such as CPR. In addition, all Nexans’s cables for building appliances under the CE mark are produced according to CPR requirements, which demands authorized third-party tests and regular inspections. We also have a menu of services, from a tutorial to a Q&A, to support our customers in understanding the regulations.
Whatever a client’s requirements, we can advise on and supply a tailored mix of fire safety cables.
“ All the megatrends lead to the same conclusion – the need for global electrification.
As a company, our intention is not only to help drive electrification but also to take decisive action to reduce our carbon footprint. ”
Christopher Guérin
Our websites
Select your country to find our products and solutions
-
Africa
- Africa
- Ghana
- Ivory Coast
- Morocco
- North West Africa
- Americas
- Asia
- Europe
- Oceania